Introduction to Smoking Alternatives
The search for useful alternatives to smoking has gained pace with increasing awareness of the health risks that come with traditional cigarette smoking. In view of 2024, the quit-smoking landscape has transformed extensively, providing various options that address different needs and wants of quitters.
The significance of finding dependable alternatives to smoking cannot be overemphasized. Millions worldwide are trying to stop this habit, and so alternatives that lower health risks should be prioritized. These can be nicotine replacement therapies or digital solutions among other things, which have different benefits and suit different types of smokers.
Looking back at how they have changed over time, it is evident that these tools have become more individualized and accessible, as seen through early nicotine gums, advanced vape pens, and up-to-date digital apps, among others, used for quitting cigarettes altogether. According to Dr. Nora Volkow, Director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, “Technological advancements along with medical science knowledge breakthroughs paved ways towards innovative aids in quitting smoking; giving new hope to people who are struggling with cessation.”
This introduction prepares us well enough to go into details about what current options exist as smoking alternatives while underscoring their innovation levels as well as effectiveness during this period leading up to 2024. In exploring these substitutes, we shall also look at how each one works, what it does best/better than others when used by whom? its advantages & disadvantages vis-à-vis other methods etcetera thus potentially transforming cessation patterns forever.
Understanding Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
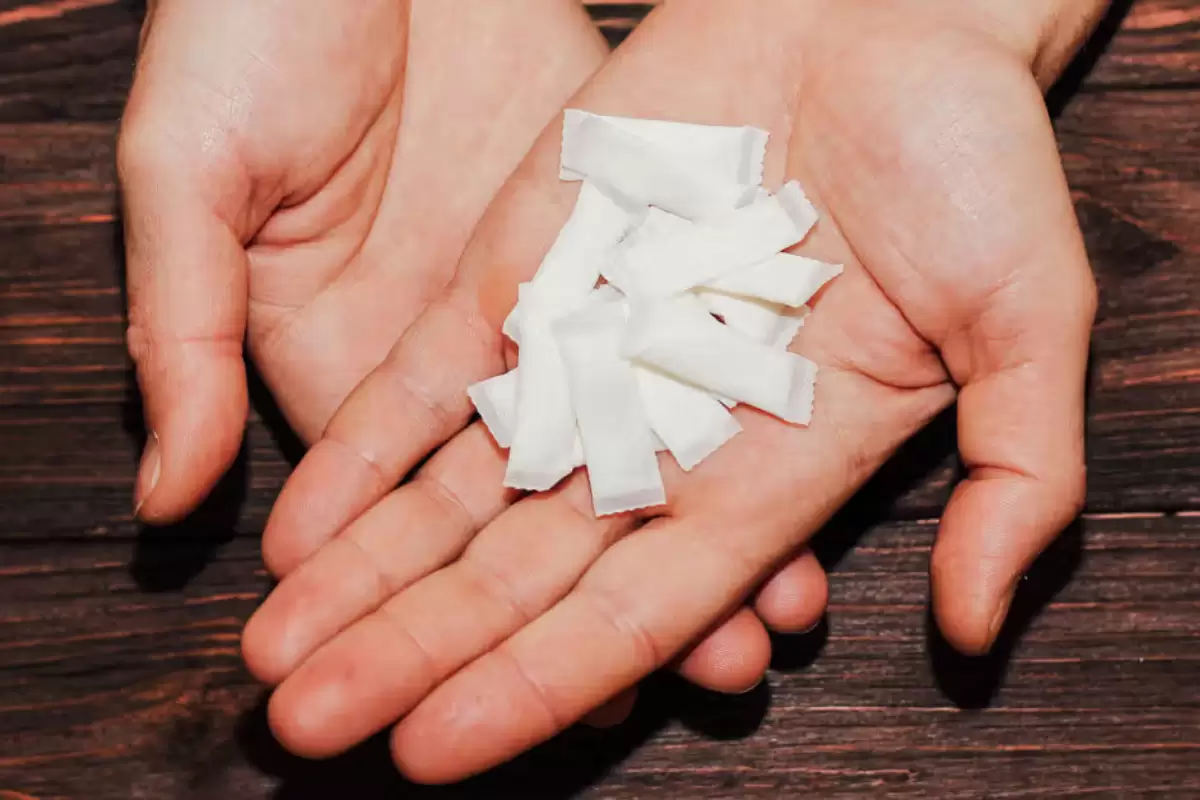
An important part of giving up smoking is Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT), which allows users to decrease their reliance on cigarettes. NRT is designed to provide smokers with medically recommended tools for reducing withdrawal symptoms. It achieves this by delivering controlled amounts of nicotine into the body without any of the other harmful chemicals found in tobacco smoke; thus assisting people who want to quit smoking.
Different forms of NRT are available depending on various smoking habits and preferences shown below:
- Nicotine patches – these stick onto your skin and release nicotine over a 24 hour period at consistent levels most suited for long-term symptomatic relief.
- Nicotine gum – This works by releasing nicotine quickly when you chew it, thereby relieving craving as needed. It helps control unexpected urges to smoke.
- Nicotine lozenges – Similar to gum but dissolves slowly in your mouth, allowing discreet usage while still delivering its nicotine content.
- Inhalers and sprays containing nicotine – These work the fastest out of all types listed here because they deliver it through lungs or nasal membranes straight into the bloodstream where it acts quickest against cravings.
Scott Gottlieb, former Commissioner of FDA, said, “No matter where they’re used or how often they’re used, NRTs increase quit rates by 50%–70%.” This statement supports their usefulness in helping individuals stop smoking.
It is important that people understand what each NRT involves if they want to use them as aids towards quitting smoking. Specific benefits come with every one but preference should be guided by personal patterns in relation to cigarette use over time; lifestyle factors also play a role so consultation with healthcare professionals would help. In this part of our conversation, we can see just how many kinds there are which replace nicotine; this shows us why these products will remain relevant even beyond 2024 when considered within scope alternatives for smoking cessation methods.
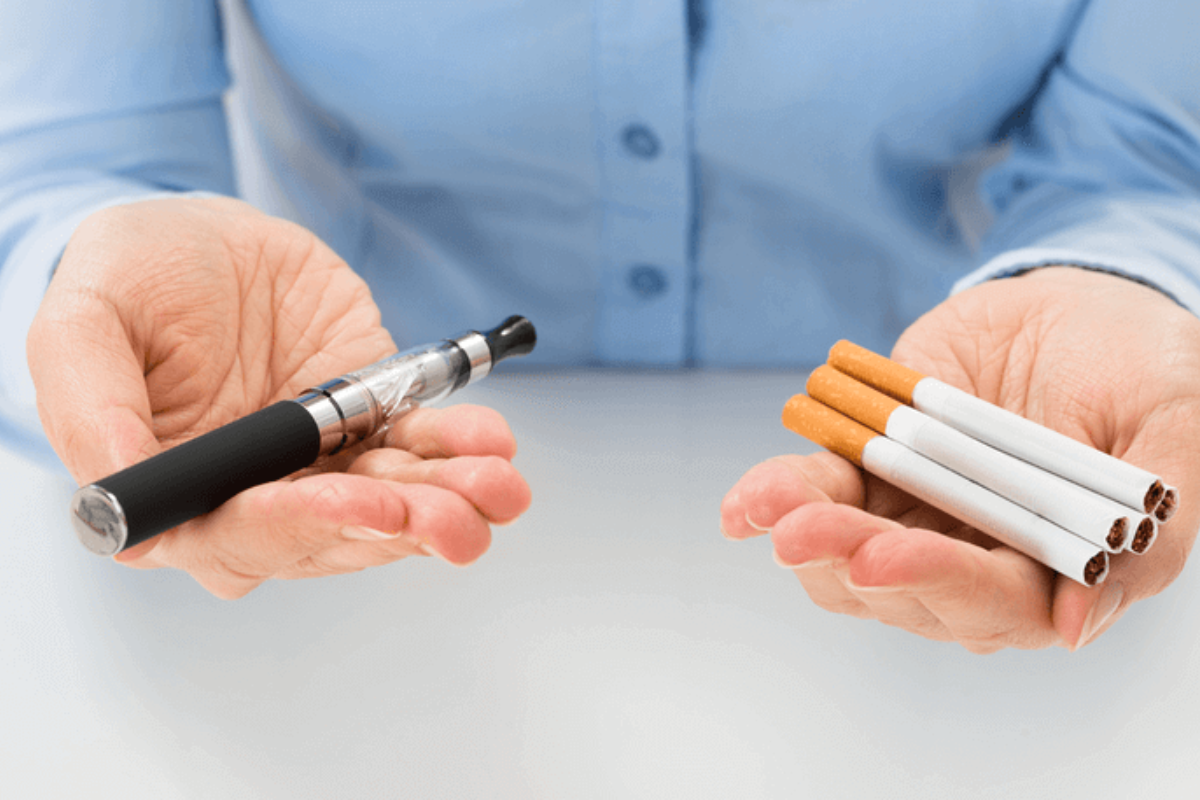
E-cigarettes as a Smoking Alternative
E-cigarettes are a popular substitute for smoking that mimic smoking without burning tobacco, generally accepted as the most common cause of preventable disease and death in developed countries. This section explores e-cigs as an option and assesses their efficacy and safety concerns.
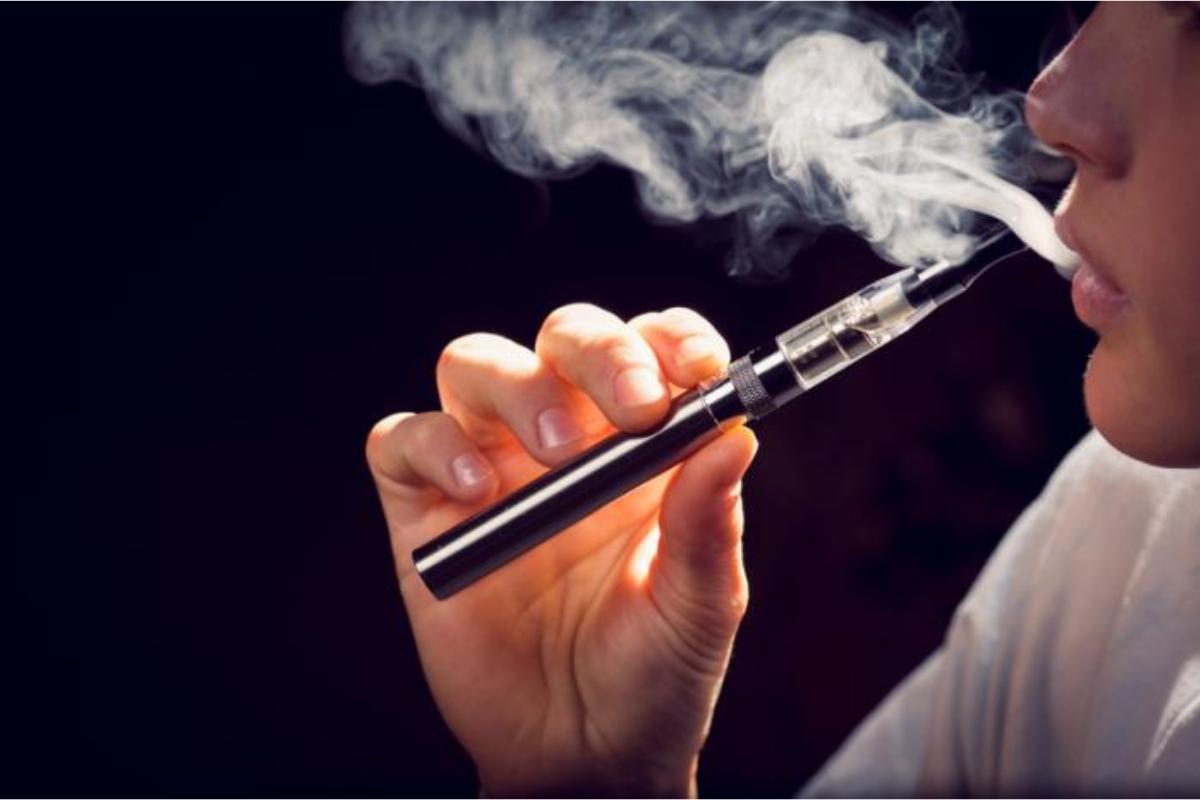
E-cigarettes work by heating a liquid – commonly called vape juice or e-liquid – containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals into an aerosol, which is inhaled by the user. The fact that no tobacco is burned greatly reduces many of the harmful compounds typically encountered in cigarette smoke. Therefore, this characteristic makes them potentially less damaging than conventional cigarettes for people who want to stop smoking.
However, whether or not they can assist people in quitting smoking is still up for debate. A study found that while some individuals find them helpful for giving up cigarettes, others may not have such success with using them this way. For adults who smoke any type of combustible tobacco product, CDC says that there is inadequate evidence at present to conclude whether or not e-cigarette use could be associated with higher quitting rates compared only when used as an entire substitute for all smoked tobacco products including but not limited to cigars, pipes, hookah, or bidis.
One concern around these products’ safety revolves around addiction potential from nicotine being delivered through inhalation rather than ingestion like traditional forms such as gum, patches, lozenges, etcetera do; also there’s worry about children becoming dependent on these substances due to their appealing flavors, packaging, etcetera. It should be noted though long-term health effects remain unknown at this time, scientific research has shown them to be less detrimental than regular cigarettes which contain carcinogens among other toxic chemicals known cause cancer, emphysema, heart disease, stroke, etcetera, so people must keep such things in mind before making any decisions about using them instead of smoking.
The current argument over where e-cigarettes fit into cessation strategies underscores the importance of additional studies clarifying their role within various methods aimed towards helping people stop tobacco use especially given new guidelines slated for release during 2024 which will shape policy regarding public health as influenced by the most recent evidence gathered from different investigations and sources.
Prescription Medications for Smoking Cessation
The quitting smoking process can be helped by prescription drugs; they are also evidence-backed substitutes for smoking. Such medicines do not only help manage the physical withdrawal symptoms from quitting but address the neurological part of nicotine addiction as well.
There are many FDA-approved prescription medications used for smoking cessation:
- Varenicline (Chantix): By blocking nicotine receptors in the brain and reducing pleasure gained through smoking, this medication eases cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Dr. John Hughes, a tobacco addiction expert, says that Varenicline is one of the most effective drugs at increasing long-term abstinence rates from smoking.
- Bupropion (Zyban): Bupropion was originally created as an antidepressant; it helps reduce cravings for nicotine and withdrawals. It is believed to do this by raising certain mood-improving brain chemicals’ levels while simultaneously suppressing appetite for tobacco.
Generally, both are given in conjunction with behavioral support as part of a comprehensive plan to quit smoking. Twice or thrice more people will succeed in quitting if these drugs are used than those who try without any pharmacological aid at all.
However, there may be side effects related to taking these medications. For instance: Mood swings and behavioral changes might occur due to Varenicline use; Bupropion should not be used by individuals with a history of seizures or heavy alcohol consumption. People ought to talk about their options with healthcare providers based on health status vis-à-vis risks versus benefits considerations.
Medically supervised care is important during alternative approaches towards stopping cigarettes because it brings out the significance of such prescribed medicines within this process. This ensures that someone has got all necessary tools needed for successfulness in giving up the smoke habit under one’s belt while at the same time getting necessary guidance on how best to utilize them during their journey towards becoming smoke-free again.
Behavioral Therapies and Support Programs
It is very important to have behavioral therapies or support programs because they are a substitute for smoking that deals with the psychological part of being addicted to cigarettes. The way that these ways work is by changing how people behave when they smoke through steps that are planned, and this has been shown to help many people stop.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is thought to be one of the most successful types of behavior therapy in helping people quit smoking. It does this by making individuals aware of what makes them want a cigarette and then teaching them different ways on how to cope when faced with such things without using nicotine. “By changing the way a person thinks about or acts toward smoking, CBT can double their likelihoods of quitting” (Timothy Baker, Ph.D., University Of Wisconsin Center For Tobacco Research And Intervention).
Another approach which may prove extremely useful is called motivational interviewing which enhances client motivation for change through resolving ambivalence about quitting. This works best in preparing smokers mentally before they start trying to quit. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, motivational interviewing can increase readiness levels necessary for giving up tobacco greatly by fostering optimistic thinking coupled with strong personal commitment towards abstinence.
To add onto these methods there are also several other elements included within cessation programs themselves like group meetings, one-on-ones, as well as digital support platforms all aimed at helping an individual along their journey towards becoming smoke-free. They provide continuing aid plus materials thus making it impossible not to use them while trying to quit successfully.
These are often supported by what are known as quit smoking programs which include things such as group sessions where people can talk about their struggles together, counseling one-on-one’s with professionals who know what they’re going through, and even mobile phone apps designed specifically for those looking to give up cigarettes once and for all but need some extra moral support during tough times. The American Cancer Society suggests taking part in these sorts of programs because not only do they offer advice from others that have already quit but also provide a sense of community and belonging which is imperative when trying to stay smoke-free for life.
It has been proven that behavioral therapies coupled together with supportive programs work very well in stopping people from smoking again even after they’ve quit. They help an individual develop new habits permanently so as never to light up another cigarette roach.
Natural and Herbal Remedies
Looking into other ways to quit smoking leads us to natural and herbal cures, which offer a holistic approach to quitting. These techniques are valued for their lack of side effects as well as being in harmony with health practices that work on the whole person.
Even St. John’s Wort, mainly utilized in the treatment of depression, is being considered for use in stopping smoking. While there isn’t much research available, some studies suggest it could help relieve psychological cravings brought about by nicotine withdrawal. Dr. Edward Barnes, a naturopathic doctor, says, “St. John’s Wort can be used alongside other holistic methods for quitting smoking but should not be relied upon alone, especially if someone wants an all-natural option.”
Another method worth mentioning is acupuncture, as many people have successfully quit this way since it helps reduce craving stress levels while going through withdrawal. Points throughout your body are pricked using super fine needles to balance out energies, promoting overall wellness according to the American Academy of Acupuncture. Many smokers have found relief from these symptoms through frequent acupuncture sessions.
Aromatherapy can also assist individuals who wish to quit inhaling smoke regularly by using certain essential oils like peppermint oil, eucalyptus oil, among others, which aid in relieving cravings and improving moods. These oils may either be diffused or applied directly onto one’s skin after being diluted first with another substance such as water or carrier oil to prevent irritation. Their calming properties make them ideal choices for those seeking natural remedies towards quitting smoking.
How successful any of these methods will work varies greatly from person to person based on how strong one’s belief system towards each particular treatment option happens to be alongside the personal level of commitment shown towards wanting success achieved through them. Dr. Barnes states, “Using more than one type together increases chances.”
The Role of Technology in Smoking Cessation
As technology is increasingly used as a way to quit smoking, heading into 2024 is no exception. Smoking cessation strategies now rely on digital tools and platforms that can reach a larger audience while still offering personalized support.
Mobile apps designed for quitting smoking have become very advanced. They can track progress, send motivational messages, and even provide personalized coaching. These apps are based on behavioral therapy principles and offer real-time assistance when users are experiencing cravings. According to the Journal of Medical Internet Research, people who use cessation apps are more likely to feel motivated and succeed in quitting overall.
Online programs are another technological development helping smokers kick the habit. These programs usually combine aspects from cognitive-behavioral therapy with those found in social support groups so that individuals can participate in community discussions and access resources at any hour of the day or night. Dr. Linda Sarna, a tobacco-free policy advocate, states: “Online cessation programs work just as well as face-to-face counseling does — especially if they provide individualized content along with interactive features.”
Future trends for technology involved in quitting smoking reveal an artificial intelligence (AI) integration combined with machine learning (ML) which will enable treatment plans customization bases on user data thus improving intervention outcomes’ VR could also be potentially used to simulate craving situations where it can be managed virtually thus changing how we train people on methods of stopping smoking.
In conclusion, technology’s application as a substitute for cigarettes continues expanding thereby making methods of quitting more effective, convenient, and adaptable to individual needs. With each passing day until 2024 these advancements will only grow further important toward enabling people to live smoke-free lives.
Common Questions About smoking alternatives
- What are smoking alternatives?
- Smoking alternatives refer to methods and products designed to help individuals reduce or quit their smoking habits. These include nicotine replacement therapies (NRTs), e-cigarettes, prescription medications, behavioral therapies, and natural remedies.
- How effective are nicotine replacement therapies (NRTs)?
- NRTs such as patches, gums, and lozenges are effective in reducing withdrawal symptoms and smoking urges. Studies show that using NRTs can double the chances of quitting smoking successfully compared to attempting to quit without any aids.
- Are e-cigarettes a safer alternative to smoking?
- E-cigarettes are considered less harmful than traditional cigarettes because they don’t produce tar or carbon monoxide, two of the most harmful elements in tobacco smoke. However, they still deliver nicotine, a highly addictive substance.
- Can prescription medications help me quit smoking?
- Yes, medications like Varenicline (Chantix) and Bupropion (Zyban) are approved for smoking cessation and have been proven to enhance the likelihood of quitting when compared to no pharmaceutical intervention. These medications work best when combined with behavioral support.
- What behavioral therapies are used to help quit smoking?
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing are common behavioral therapies that help modify a person’s behaviors and attitudes towards smoking. They focus on providing strategies to cope with cravings and triggers.
- Are there any natural methods to quit smoking?
- Some individuals find relief in natural methods like acupuncture, herbal supplements, or aromatherapy, although these are generally considered complementary approaches and should ideally be combined with more conventional methods.
- What role does technology play in smoking cessation?
- Technology, especially mobile apps and online programs, plays a significant role in supporting smokers through quit programs. These digital tools offer resources such as tracking systems, educational content, and community support, which are accessible and customizable.
Here are five scholarly articles related to smoking alternatives, focusing on different aspects of smoking cessation and the efficacy of various interventions:
- “Consideration of vaping products as an alternative to adult smoking: a narrative review” – This article explores the role of e-cigarettes as a smoking alternative, discussing their toxicology and the reduction of harmful components compared to traditional cigarette smoke. It details studies on the reduced toxicity of e-cigarette aerosol in biological systems (BioMed Central).
- “Impact of tobacco and/or nicotine products on health and functioning: a scoping review and findings from the preparatory phase of the development of a new self-report measure” – This comprehensive review examines the health impacts of tobacco and nicotine products, focusing on user experiences and the development of new metrics for assessing harm reduction in tobacco use (BioMed Central).
- “Non-pharmacological interventions for smoking cessation: analysis of systematic reviews and meta-analyses” – This article reviews various non-pharmacological strategies for smoking cessation, analyzing their effectiveness through systematic reviews and meta-analyses. It discusses different behavioral interventions and their impacts on quitting smoking (BioMed Central).
- “Effectiveness of stop smoking interventions among adults: protocol for an overview of systematic reviews and an updated systematic review” – This study outlines a protocol for reviewing the effectiveness of smoking cessation interventions, including electronic cigarettes and behavioral therapies, providing a structured approach to evaluating existing research (BioMed Central).